Library for Mini-DK board
Dependents: LPC1768_Mini-DK_EasyWeb_DM9161 LPC1768_Mini-DK LPC1768_Mini-DK
Fork of Mini-DK by
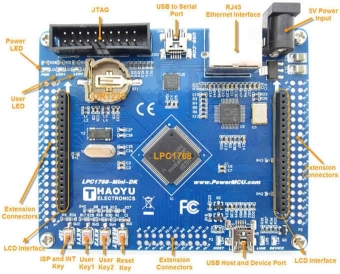
Mini-DK board overview (Micro SD connector is at the bottom side)
One serial interface , uses CP2102 (USB to RS232 interface, support ISP download )
RJ45-10/100M Ethernet network interface (Ethernet PHY: DM9161)
2.8 inch TFT color LCD interface (SPI interface or 16Bit parallel interface)
Touch panel controller XPT2046 (ADS7843 compatible)
USB 2.0 interface, USB host and USB Device interface.
TF SD / MMC card (SPI) interface.
Two user buttons, One Reset button and ISP button , One INT0 button, two user-programmable LED lights
Serial ISP download, Standard 20-pin JTAG download simulation debugging interface.
Selection between external 5V power supply or USB 5V supply.
Board size: 95mm * 78mm
All IO available on extension connectors
04/01/13
Erik Olieman (http://mbed.org/users/Sissors/) joined the code development for the Mini-DK board.
Thanks to his input, we were able to obtain a tremendous speed gain, remove warnings, ...
An overview of all modifications is stored in modifs.h
The old page (http://mbed.org/users/frankvnk/code/LPC1768_Mini-DK/) contains the demo code.
IMPORTANT : Due to a change in the mbed libraries (Stream()), we cannot use the printf instruction - we need to use <SPI_TFT>.printf (example - see main.cpp in http://mbed.org/users/frankvnk/code/LPC1768_Mini-DK/)
WARNING: filetoflash (SD to CPU flash)
The SPI_TFT library contains an option to copy an image from the SD card to the CPU flash memory. This allows you to use an image as background without speed loss when writing other text and graphics.
By default, this option is enabled.
It can be disabled by uncommenting the #define mentioned below in Mini_DK.h:
#define NO_FLASH_BUFFER
Since the flash memory has limited write endurance, DO NOT use this feature when you intend to read multiple images from the SD card (eg: when used as a photo frame).
14/01/13
A newer version of the Mini-DK has been released by the manufacturer: Mini-DK2. They replaced the DM9161 PHY with a LAN8720A PHY and better buttons are fitted on the board. All other hardware remains the same. Code for this PHY is available from the NXP MCU SW application team. This allows us to use the mbed 'EthernetInterface' library with little modifications. Further info - see http://mbed.org/forum/mbed/topic/3684/?page=1#comment-18473.
Notes:
The code in 'lpc_phy_lan8720.c' uses 'msDelay' - needs to be replaced with 'osDelay'.
A custom MAC address can be defined using following code:
extern "C" void mbed_mac_address(char * mac) {
// define your own MAC Address
mac[0] = 0x00;
mac[1] = 0x01;
mac[2] = 0x02;
mac[3] = 0x03;
mac[4] = 0x04;
mac[5] = 0x05;
};
Diff: SPI_TFT/IAP/IAP.cpp
- Revision:
- 18:f045ae645960
- Parent:
- 17:66c4e84d8571
- Child:
- 19:6816fa47b39e
--- a/SPI_TFT/IAP/IAP.cpp Wed Jan 09 20:54:35 2013 +0000
+++ /dev/null Thu Jan 01 00:00:00 1970 +0000
@@ -1,271 +0,0 @@
-/** IAP : internal Flash memory access library
- *
- * The internal Flash memory access is described in the LPC1768 and LPC11U24 usermanual.
- * http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10360.pdf
- * http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10462.pdf
- *
- * LPC1768 --
- * Chapter 2: "LPC17xx Memory map"
- * Chapter 32: "LPC17xx Flash memory interface and programming"
- * refering Rev. 01 - 4 January 2010
- *
- * LPC11U24 --
- * Chapter 2: "LPC11Uxx Memory mapping"
- * Chapter 20: "LPC11Uxx Flash programming firmware"
- * refering Rev. 03 - 16 July 2012
- *
- * Released under the MIT License: http://mbed.org/license/mit
- *
- * revision 1.0 09-Mar-2010 1st release
- * revision 1.1 12-Mar-2010 chaged: to make possible to reserve flash area for user
- * it can be set by USER_FLASH_AREA_START and USER_FLASH_AREA_SIZE in IAP.h
- * revision 2.0 26-Nov-2012 LPC11U24 code added
- * revision 2.1 26-Nov-2012 EEPROM access code imported from Suga koubou san's (http://mbed.org/users/okini3939/) library
- * http://mbed.org/users/okini3939/code/M0_EEPROM_test/
- */
-
-#include "mbed.h"
-#include "IAP.h"
-
-#define USER_FLASH_AREA_START_STR( x ) STR( x )
-#define STR( x ) #x
-
-unsigned char user_area[ USER_FLASH_AREA_SIZE ] __attribute__((section( ".ARM.__at_" USER_FLASH_AREA_START_STR( USER_FLASH_AREA_START ) ), zero_init));
-
-
-/*
- * Reserve of flash area is explained by Igor. Please refer next URL
- * http://mbed.org/users/okano/notebook/iap-in-application-programming-internal-flash-eras/?page=1#comment-271
- */
-
-//unsigned char user_area[ size ] __attribute__((section(".ARM.__at_0x78000"), zero_init));
-
-/*
- * IAP command codes
- * Table 589. "IAP Command Summary", Chapter 8. "IAP commands", usermanual
- */
-
-enum command_code
- {
- IAPCommand_Prepare_sector_for_write_operation = 50,
- IAPCommand_Copy_RAM_to_Flash,
- IAPCommand_Erase_sector,
- IAPCommand_Blank_check_sector,
- IAPCommand_Read_part_ID,
- IAPCommand_Read_Boot_Code_version,
- IAPCommand_Compare,
- IAPCommand_Reinvoke_ISP,
- IAPCommand_Read_device_serial_number,
-#if defined(TARGET_LPC11U24)
- IAPCommand_EEPROM_Write = 61,
- IAPCommand_EEPROM_Read,
-#endif
- };
-
-
-/** Read part identification number
- *
- * @return device ID
- * @see read_serial()
- */
-
-int IAP::read_ID( void ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Read_part_ID;
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- // return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 1 ] ); // to return the number itself (this command always returns CMD_SUCCESS)
-}
-
-
-/** Read device serial number
- *
- * @return device serial number
- * @see read_ID()
- */
-
-int IAP::read_serial( void ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Read_device_serial_number;
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- // return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 1 ] ); // to return the number itself (this command always returns CMD_SUCCESS)
-}
-
-
-/** Blank check sector(s)
- *
- * @param start a Start Sector Number
- * @param end an End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number).
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | BUSY | SECTOR_NOT_BLANK | INVALID_SECTOR
- */
-
-int IAP::blank_check( int start, int end ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Blank_check_sector;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)start; // Start Sector Number
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)end; // End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number)
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-
-/** Erase Sector(s)
- *
- * @param start a Start Sector Number
- * @param end an End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number).
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | BUSY | SECTOR_NOT_PREPARED_FOR_WRITE_OPERATION | INVALID_SECTOR
- */
-
-int IAP::erase( int start, int end ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Erase_sector;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)start; // Start Sector Number
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)end; // End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number)
- IAP_command[ 3 ] = cclk_kHz; // CPU Clock Frequency (CCLK) in kHz
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-
-/** Prepare sector(s) for write operation
- *
- * @param start a Start Sector Number
- * @param end an End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number).
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | BUSY | INVALID_SECTOR
- */
-
-int IAP::prepare( int start, int end ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Prepare_sector_for_write_operation;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)start; // Start Sector Number
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)end; // End Sector Number (should be greater than or equal to start sector number).
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-
-/** Copy RAM to Flash
- *
- * @param source_addr Source RAM address from which data bytes are to be read. This address should be a word boundary.
- * @param target_addr Destination flash address where data bytes are to be written. This address should be a 256 byte boundary.
- * @param size Number of bytes to be written. Should be 256 | 512 | 1024 | 4096.
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | SRC_ADDR_ERROR (Address not a word boundary) | DST_ADDR_ERROR (Address not on correct boundary) | SRC_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED | DST_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED | COUNT_ERROR (Byte count is not 256 | 512 | 1024 | 4096) | SECTOR_NOT_PREPARED_FOR_WRITE_OPERATION | BUSY
- */
-
-int IAP::write( char *source_addr, char *target_addr, int size ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Copy_RAM_to_Flash;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)target_addr; // Destination flash address where data bytes are to be written. This address should be a 256 byte boundary.
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)source_addr; // Source RAM address from which data bytes are to be read. This address should be a word boundary.
- IAP_command[ 3 ] = size; // Number of bytes to be written. Should be 256 | 512 | 1024 | 4096.
- IAP_command[ 4 ] = cclk_kHz; // CPU Clock Frequency (CCLK) in kHz.
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-
-/** Compare <address1> <address2> <no of bytes>
- *
- * @param source_addr Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- * @param target_addr Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- * @param size Number of bytes to be compared; should be a multiple of 4.
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | COMPARE_ERROR | COUNT_ERROR (Byte count is not a multiple of 4) | ADDR_ERROR | ADDR_NOT_MAPPED
- */
-
-int IAP::compare( char *source_addr, char *target_addr, int size ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_Compare;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)target_addr; // Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)source_addr; // Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- IAP_command[ 3 ] = size; // Number of bytes to be compared; should be a multiple of 4.
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-/** Compare <address1> <address2> <no of bytes>
- *
- * @param source_addr Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- * @param target_addr Starting flash or RAM address of data bytes to be compared. This address should be a word boundary.
- * @param size Number of bytes to be compared; should be a multiple of 4.
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | COMPARE_ERROR | COUNT_ERROR (Byte count is not a multiple of 4) | ADDR_ERROR | ADDR_NOT_MAPPED
- */
-
-int IAP::read_BootVer(void) {
- IAP_command[0] = IAPCommand_Read_Boot_Code_version;
- IAP_result[1] = 0; // not sure if in high or low bits.
- iap_entry(IAP_command, IAP_result);
- return ((int)IAP_result[1]);
-}
-
-/** Get user reserved flash start address
- *
- * @return start address of user reserved flash memory
- * @see reserved_flash_area_size()
- */
-
-char * IAP::reserved_flash_area_start( void )
-{
- return ( (char *)USER_FLASH_AREA_START );
-}
-
-
-/** Get user reserved flash size
- *
- * @return size of user reserved flash memory
- * @see reserved_flash_area_start()
- */
-
-int IAP::reserved_flash_area_size( void )
-{
- return ( USER_FLASH_AREA_SIZE );
-}
-
-#if defined(TARGET_LPC11U24)
-/** Copy RAM to EEPROM (LPC11U24)
- *
- * @param source_addr Source RAM address from which data bytes are to be read.
- * @param target_addr Destination EEPROM address where data bytes are to be written.
- * @param size Number of bytes to be written.
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | SRC_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED | DST_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED
- * Remark: The top 64 bytes of the EEPROM memory are reserved and cannot be written to.
- */
-int IAP::write_eeprom( char *source_addr, char *target_addr, int size ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_EEPROM_Write;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)target_addr; // Destination EEPROM address where data bytes are to be written. This address should be a 256 byte boundary.
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)source_addr; // Source RAM address from which data bytes are to be read. This address should be a word boundary.
- IAP_command[ 3 ] = size; // Number of bytes to be written. Should be 256 | 512 | 1024 | 4096.
- IAP_command[ 4 ] = cclk_kHz; // CPU Clock Frequency (CCLK) in kHz.
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-
-/** Copy EEPROM to RAM (LPC11U24)
- *
- * @param source_addr Source EEPROM address from which data bytes are to be read.
- * @param target_addr Destination RAM address where data bytes are to be written.
- * @param size Number of bytes to be written.
- * @return error code: CMD_SUCCESS | SRC_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED | DST_ADDR_NOT_MAPPED
- * Remark: The top 64 bytes of the EEPROM memory are reserved and cannot be written to.
- */
-int IAP::read_eeprom( char *source_addr, char *target_addr, int size ) {
- IAP_command[ 0 ] = IAPCommand_EEPROM_Read;
- IAP_command[ 1 ] = (unsigned int)source_addr; // Source EEPROM address from which data bytes are to be read. This address should be a word boundary.
- IAP_command[ 2 ] = (unsigned int)target_addr; // Destination RAM address where data bytes are to be written. This address should be a 256 byte boundary.
- IAP_command[ 3 ] = size; // Number of bytes to be written. Should be 256 | 512 | 1024 | 4096.
- IAP_command[ 4 ] = cclk_kHz; // CPU Clock Frequency (CCLK) in kHz.
-
- iap_entry( IAP_command, IAP_result );
-
- return ( (int)IAP_result[ 0 ] );
-}
-#endif


