Bug fix release
Dependents: AntiTheftGPS XbeeReceive XbeeSend Superball_Ball2 ... more
MODSERIAL is an easy to use library that extends Serial to add fully buffered input and output.
The features of MODSERIAL include:-
- Directly compatible with Serial
- Fully customisable buffer settings
- Current buffer information via the API
- Circular buffers that allow for dynamic compile-time and/or run-time resizing
- Bulk buffer sending using MODDMA GPDMA direct memory to peripheral data transfers.
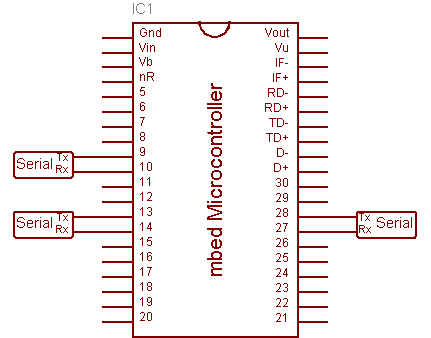
Connecting up the MODSERIAL module
The starting point for using MODSERIAL is the Mbed's own handbook for Serial library object. MODSERIAL inherits Serial and adds extensions for buffering. So getting started is easy. Follow the Mbed instructions for Serial to get setup. Here's a reproduction of Serial's simple code starter:-
1 #include "mbed.h"
2
3 Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
4
5 int main() {
6 pc.printf("Hello World!");
7 while(1) {
8 pc.putc(pc.getc() + 1);
9 }
10 }
All we need to do to use MODSERIAL is to add a #include and alter one line thus:-
1 #include "mbed.h"
2 #include "MODSERIAL.h"
3 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
4
5 int main() {
6 pc.printf("Hello World!");
7 while(1) {
8 pc.putc(pc.getc() + 1);
9 }
10 }
As we can see, all we have done is add the header at line 2 and changed line 3 to specify the use of MODSERIAL in replacement for Serial. The default settings for MODSERIAL are that both the TX and RX buffers are assigned 256 bytes each of storage space. This storage space is acquired from the heap using malloc.
The default buffer assignment can be manipulated in three ways. First is the compile time setting which alters the default parameters used when creating a MODSERIAL object. This is done thus:-
1 #include "mbed.h" 2 3 #define MODSERIAL_DEFAULT_RX_BUFFER_SIZE 512 4 #define MODSERIAL_DEFAULT_TX_BUFFER_SIZE 1024 5 #include "MODSERIAL.h" 6 7 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx 8 ...
By defining the two #defines before the #include "MODSERIAL.h" alters the defaults MODSERIAL uses to create it's buffers.
The second method is the run-time version. To get TX at 1024 and RX buffer at 512 as above during run-time initialisation, alter the constructor thus:-
1 #include "mbed.h" 2 #include "MODSERIAL.h" 3 4 // Make TX buffer 1024bytes and RX buffer use 512bytes. 5 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX, 1024, 512); // tx, rx 6 ...
If you supply only one numeric value, as shown below, both TX and RX will have the same buffer sizes assigned to them:-
1 #include "mbed.h" 2 #include "MODSERIAL.h" 3 4 // Make both TX and RX use a 512byte buffer. 5 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX, 512); // tx, rx 6 ...
The third method is reassigning a new buffer while the program is running. This allows the program to grow and shrink either buffer as required. However, there are caveats to do this as will be shown below.
First, expanding the buffer involves increasing the buffer size. This is fairly straight forward and is accomplished thus:-
1 #include "mbed.h"
2 #include "MODSERIAL.h"
3 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
4
5 int main() {
6
7 // Increase the TX buffer from the default 256bytes to 1024bytes.
8 if (pc.txBufferSetSize(1024) != MODSERIAL::Ok) {
9 error("Failed to allocate memory for new buffer");
10 }
11
12 pc.printf("Hello World!");
13 while(1) {
14 pc.putc(pc.getc() + 1);
15 }
16 }
As can be seen, growing the buffer is fairly straight forward. However, how it is done should be understood by the user. First, a new buffer allocation is made using malloc. Once acquired the current buffer is checked for contents. If the current buffer is not empty it is copied to the new buffer so the old buffer contents is maintained after resizing. The last step is then to free() the old memory buffer.
The buffer can also be contracted to a smaller length buffer. Here's the code:-
1 #include "mbed.h"
2 #include "MODSERIAL.h"
3 MODSERIAL pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
4
5 int main() {
6 int result;
7
8 // Decrease the TX buffer from the default 256bytes to 32bytes.
9 result = pc.txBufferSetSize(32);
10 if (result != MODSERIAL::Ok) {
11 switch(result) {
12 case MODSERIAL::BufferOversize:
13 error("Contents too big to fit into new allocation");
14 break;
15 case MODSERIAL::NoMemory:
16 error("Not enough memory for new allocation");
17 break;
18 }
19 }
11
12 pc.printf("Hello World!");
13 while(1) {
14 pc.putc(pc.getc() + 1);
15 }
16 }
Since buffer resizing involves the copying over of any existing old buffer contents the possibility exists that the current buffer contains more bytes than will fit into the new requested buffer. In these conditions the user must handle the return value of the resize functions. If the contents are of no concern then calling txBufferFlush() to empty of the contents before resizing.
MODSERIAL Interrupts
Users of Serial will be familar with the fact that you can attach functions or methods to TxIrq or RxIrq. This attachment of callbacks allows users to have Interrupt Service Routines (ISR) for both the TX and RX channel of the Uart. MODSERIAL uses both of these callbacks to maintain it's buffers and so are not available to users. However, MODSERIAL does contain five potential callbacks the user can use. These are:-
- TxIrq - This callback is used to inform the user's program that a character was transferred from the TX buffer to the Uart's TX THR FIFO.
- RxIrq - This callback is used to inform the user's program that a character was transferred from the Uart's RX FIFO RBR to the RX buffer.
- RxOvIrq - This callback is used to inform the user's program that a character in the Uart's RX FIFO RBR failed to transfer to the RX buffer because the RX buffer was full. The failed byte is availble via xxGetLastChar() methods.
- TxOvIrq - As RX overflow above
- TxEmpty - This callback is made when the last byte in the TX buffer is transferred to the Uart's TX THR FIFO. It informs the user's program that the TX buffer has become empty. However, it does not mean transmission is complete. See the example1.cpp example for more information.
Delineating "packets"
Many devices send information on RS232 interfaces in distinct "packets". As an example of this is NMEA information sent by many GPS modules. Each NMEA sentence is delineated by a '\n' newline character. Each sentence can be of vary length depending upon the information being sent, however, all are seperated by a '\n' newline. Detecting this if very simple with MODSERIAL. Here's an example:-
#include "mbed.h"
#include "MODSERIAL.h"
// Connect the TX of the GPS module to p10 RX input
MODSERIAL gps(NC, p10);
bool newline_detected = false;
// Called everytime a new character goes into
// the RX buffer. Test that character for \n
// Note, rxGetLastChar() gets the last char that
// we received but it does NOT remove it from
// the RX buffer.
void rxCallback(MODSERIAL_IRQ_INFO *q) {
MODSERIAL *serial = q->serial;
if ( serial->rxGetLastChar() == '\n') {
newline_detected = true;
}
}
int main() {
gps.baud(9600);
gps.attach(&rxCallback, MODSERIAL::RxIrq);
// Wait here until we detect the \n going into the buffer.
while (! newline_detected ) ;
// When we get here the RX buffer now contains a NMEA sentence.
// ...
}
Note, the txGetLastChar() and rxGetLastChar() methods only return the last character but they do not remove that character from the associated buffer.
If this is your first time using MODSERIAL or would just like to test it out then see the example.cpp that comes with the library.
DMA.cpp@3:0f10f536456e, 2010-11-21 (annotated)
- Committer:
- AjK
- Date:
- Sun Nov 21 13:58:53 2010 +0000
- Revision:
- 3:0f10f536456e
1.4
Who changed what in which revision?
| User | Revision | Line number | New contents of line |
|---|---|---|---|
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 1 | /* |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 2 | Copyright (c) 2010 Andy Kirkham |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 3 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 4 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 5 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 6 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 7 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 8 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 9 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 10 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 11 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 12 | all copies or substantial portions of the Software. |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 13 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 14 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 15 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 16 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 17 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 18 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 19 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 20 | THE SOFTWARE. |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 21 | */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 22 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 23 | #include "MODSERIAL.h" |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 24 | #include "MACROS.h" |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 25 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 26 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_ENABLE 1 |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 27 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 28 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART0_TX (8UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 29 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART0_RX (9UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 30 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART1_TX (10UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 31 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART1_RX (11UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 32 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART2_TX (12UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 33 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART2_RX (13UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 34 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART3_TX (14UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 35 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_UART3_RX (15UL << 1) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 36 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART0_TX (8UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 37 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART0_RX (9UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 38 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART1_TX (10UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 39 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART1_RX (11UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 40 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART2_TX (12UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 41 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART2_RX (13UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 42 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART3_TX (14UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 43 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART3_RX (15UL << 6) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 44 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 45 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_INC (1UL << 26) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 46 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_DST_INC (1UL << 27) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 47 | #define DMA_CHANNEL_TCIE (1UL << 31) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 48 | #define DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_M2M (0UL << 11) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 49 | #define DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_M2P (1UL << 11) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 50 | #define DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_P2M (2UL << 11) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 51 | #define DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_P2P (3UL << 11) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 52 | #define DMA_MASK_IE (1UL << 14) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 53 | #define DMA_MASK_ITC (1UL << 15) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 54 | #define DMA_LOCK (1UL << 16) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 55 | #define DMA_ACTIVE (1UL << 17) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 56 | #define DMA_HALT (1UL << 18) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 57 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 58 | namespace AjK { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 59 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 60 | extern "C" void isr_dma_core(void); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 61 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 62 | class MODSERIAL *modserial_this[4] = { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 63 | (class MODSERIAL *)NULL, |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 64 | (class MODSERIAL *)NULL, |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 65 | (class MODSERIAL *)NULL, |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 66 | (class MODSERIAL *)NULL }; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 67 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 68 | uint32_t old_dma_vector = 0; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 69 | typedef void (*MODSERIALFN)(void); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 70 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 71 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 72 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 73 | int |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 74 | MODSERIAL::dmaSend(char *buffer, int length, dmaChannel q) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 75 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 76 | LPC_GPDMACH_TypeDef *dma_base = dmaSetup(q); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 77 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 78 | switch( _uidx ) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 79 | case 0: LPC_UART0->DMAREQSEL &= ~(1UL << 0) & 0xFF; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 80 | case 1: LPC_UART0->DMAREQSEL &= ~(1UL << 2) & 0xFF; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 81 | case 2: LPC_UART0->DMAREQSEL &= ~(1UL << 4) & 0xFF; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 82 | case 3: LPC_UART0->DMAREQSEL &= ~(1UL << 6) & 0xFF; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 83 | default: error("No _uidx to request select for DMA UART peripheral destination."); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 84 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 85 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 86 | dma_base->DMACCSrcAddr = (uint32_t)buffer; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 87 | dma_base->DMACCDestAddr = (uint32_t)_base + MODSERIAL_THR; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 88 | dma_base->DMACCLLI = 0; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 89 | dma_base->DMACCControl = DMA_CHANNEL_TCIE | DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_INC | (uint32_t)length; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 90 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 91 | uint32_t DestPeripheral = DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART0_TX; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 92 | switch ( _uidx ) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 93 | case 0: DestPeripheral = DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART0_TX; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 94 | case 1: DestPeripheral = DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART1_TX; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 95 | case 2: DestPeripheral = DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART2_TX; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 96 | case 3: DestPeripheral = DMA_CHANNEL_DST_PERIPHERAL_UART3_TX; break; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 97 | default: error("No _uidx to identify DMA peripheral destination."); // Redundent. |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 98 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 99 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 100 | /* Enable SSP0 DMA. */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 101 | //LPC_SSP0->DMACR = 0x3; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 102 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 103 | // Enable Channel |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 104 | dma_base->DMACCConfig = DMA_CHANNEL_ENABLE | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 105 | DestPeripheral | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 106 | DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_M2P | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 107 | DMA_MASK_IE | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 108 | DMA_MASK_ITC; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 109 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 110 | /* Wait until at least one byte has arrived into the RX FIFO |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 111 | and then start-up the Channel1 DMA to begin transferring them. */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 112 | // while((LPC_SSP0->SR & (1UL << 2)) == 0); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 113 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 114 | /* Enable Channel1 */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 115 | /* |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 116 | LPC_GPDMACH1->DMACCConfig = DMA_CHANNEL_ENABLE | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 117 | DMA_CHANNEL_SRC_PERIPHERAL_SSP0_RX | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 118 | DMA_TRANSFER_TYPE_P2M | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 119 | DMA_MASK_IE | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 120 | DMA_MASK_ITC; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 121 | */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 122 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 123 | /* SSP0 CS line and "page_read_in_progress" flag are now |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 124 | under DMA/SSP0 interrupt control. See the DMA ISR handlers |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 125 | and SSP0 ISR handlers for more information. */ |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 126 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 127 | return 1; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 128 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 129 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 130 | void |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 131 | MODSERIAL::isr_tx_dma(void) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 132 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 133 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 134 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 135 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 136 | void |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 137 | MODSERIAL::isr_rx_dma(void) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 138 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 139 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 140 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 141 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 142 | LPC_GPDMACH_TypeDef * |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 143 | MODSERIAL::dmaSetup(dmaChannel q) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 144 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 145 | if (LPC_SC->PCONP & (1UL << 29) == 0 ) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 146 | LPC_SC->PCONP |= (1UL << 29); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 147 | LPC_GPDMA->DMACConfig = 1; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 148 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 149 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 150 | if ( old_dma_vector == NULL ) old_dma_vector = NVIC_GetVector(DMA_IRQn); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 151 | NVIC_SetVector(DMA_IRQn, (uint32_t)isr_dma_core); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 152 | NVIC_EnableIRQ(DMA_IRQn); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 153 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 154 | modserial_this[_uidx] = this; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 155 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 156 | LPC_GPDMA->DMACIntTCClear = (1UL << (int)dmaInUse); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 157 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 158 | LPC_GPDMACH_TypeDef *dma_base = dmaSelectChannel( q ); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 159 | return dma_base; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 160 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 161 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 162 | void |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 163 | MODSERIAL::this_reset(void) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 164 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 165 | modserial_this[_uidx] = (class MODSERIAL *)NULL; |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 166 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 167 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 168 | extern "C" void isr_dma_core(void) |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 169 | { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 170 | for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 171 | if (modserial_this[i] != (class MODSERIAL *)NULL) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 172 | if (modserial_this[i]->dmaInUse[MODSERIAL::RxIrq] != MODSERIAL::NotInUse) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 173 | modserial_this[i]->isr_rx_dma(); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 174 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 175 | if (modserial_this[i]->dmaInUse[MODSERIAL::TxIrq] != MODSERIAL::NotInUse) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 176 | modserial_this[i]->isr_tx_dma(); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 177 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 178 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 179 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 180 | if (old_dma_vector) { |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 181 | ((MODSERIALFN)old_dma_vector)(); |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 182 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 183 | } |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 184 | |
| AjK | 3:0f10f536456e | 185 | }; // namespace AjK ends |
 Andy K
Andy K